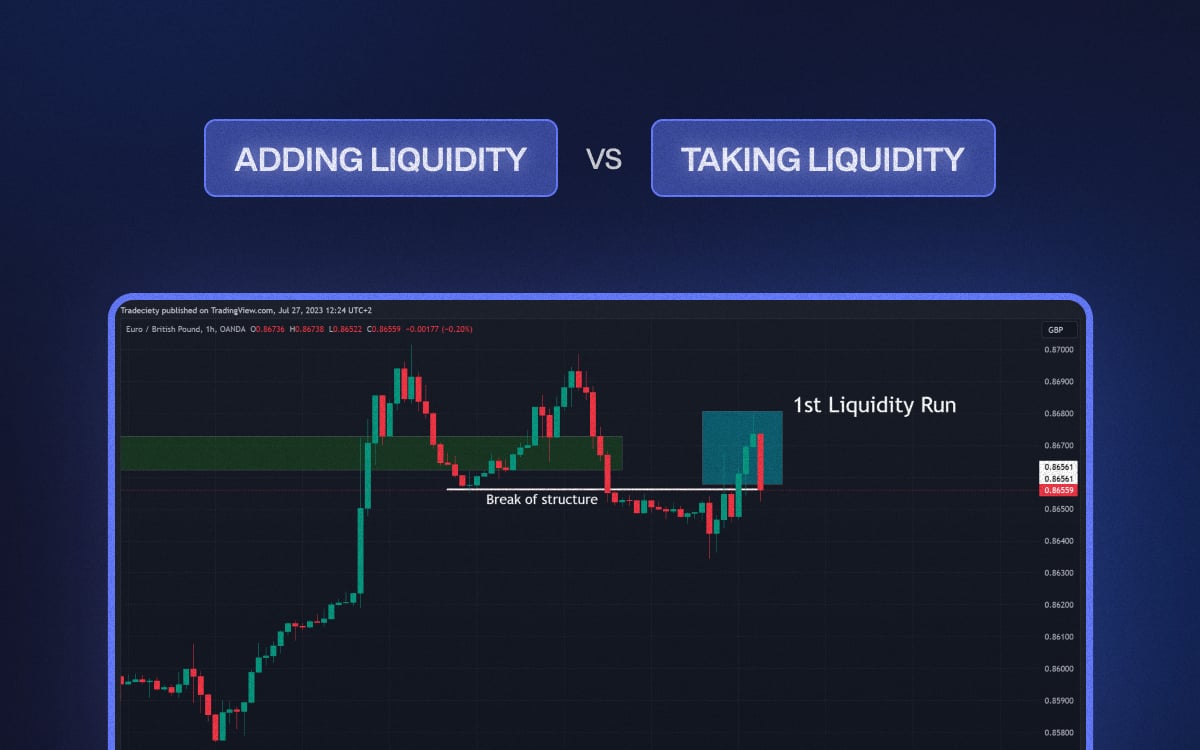
Liquidity is an important concept in trading, as it refers to the ease with which an asset can be bought or sold. Adding liquidity and taking liquidity are two different strategies that traders use to take advantage of market conditions.
Adding liquidity involves providing liquidity to the market by placing buy or sell orders. Taking liquidity involves taking liquidity away from the market by placing orders that match existing orders.
Both strategies can generate profits but come with different risks and rewards.
What is liquidity in trading markets?
To understand liquidity property, we must first understand two trading terms: bid and ask.
The bid is the highest price a buyer is willing to pay for a security at a given moment. It represents the demand side of the market. On the other hand, ask (or Offer) is the lowest price a seller is willing to accept for a security. It represents the supply side of the market.
Liquidity, in the context of bid and ask prices, refers to the ease with which a security can be bought or sold in the market without significantly affecting its price.
In a highly liquid market, many buyers and sellers actively trade security. This typically means a smaller bid-ask spread. For example, if the current bid price for a stock is $50 and the ask price is $50.05, the bid-ask spread is narrow ($0.05).
Conversely, in a market with low liquidity, there are fewer buyers and sellers, resulting in wider bid-ask spreads. For instance, if the bid price for a stock is $50 and the ask price is $51, the bid-ask spread is wider ($1).
What is adding liquidity to the market?
Adding liquidity to a market means a trader provides liquidity by placing buy or sell orders. This increases the number of buyers and sellers in the market, making it easier for other traders to buy or sell the asset.
This type of order is often called a “market order” and is used to quickly fill a trader’s position. By adding liquidity to the market, traders can benefit from the increased trading volume and liquidity their orders bring.
This can lead to more efficient price discovery and better execution of trades. Additionally, adding liquidity can help reduce the spread between the bid and ask prices, resulting in lower trading costs.
It can also reduce transaction costs, as buying and selling assets is easier without causing large price movements. However, there are some caveats to this general rule.
For example, if liquidity is added to a market that is already highly liquid, it may not have a significant impact on volatility. Additionally, if liquidity is added to a market that is already highly volatile, it may not reduce volatility.
What is taking liquidity from the market?
Taking liquidity from a market means that a trader is removing liquidity from the market by taking the other side of a buy or sell order. This reduces the number of buyers and sellers in the market, making it more difficult for other traders to buy or sell the asset.
This type of order is often called a “limit order” and is used to take advantage of price discrepancies in the market. By taking liquidity, traders can benefit from the price difference between their order and the current market price.
This can lead to higher profits, but it also carries the risk of not being filled if the market moves against the trader’s position.
Second, taking liquidity can lead to slippage. Slippage occurs when the price of an asset moves against the trader before the order is filled. This can lead to losses if the price moves too far away from the trader’s entry point.
Third, taking liquidity can lead to increased costs. When traders take liquidity, they essentially pay for the privilege of entering the market.
This can lead to higher transaction costs as you pay for the liquidity you’re taking away from the market.
Analyzing the Risks of Adding Liquidity in Trading
Adding liquidity to a trading market can be a risky endeavor. Liquidity is the ability of a market to accept large orders without significantly affecting the price of the asset being traded.
When liquidity is low, it can be difficult to enter or exit a position without incurring large losses. Adding liquidity to a market can be risky, exposing traders to significant losses if the market moves against them.
The most significant risk is the potential for large losses if the market moves against the trader. This risk is especially pronounced in markets with low liquidity, as the lack of buyers and sellers can cause prices to move quickly and unexpectedly.
Additionally, traders must consider the potential for slippage, which is the difference between the expected price of a trade and the actual price at which the trade is executed. Slippage can occur when there is a lack of liquidity in the market, as the trader may not be able to find a buyer or seller at the expected price.
The next thing you must consider is the potential for counterparty risk. Counterparty risk is the risk that the other party in the trade will not fulfill their obligations. This risk is especially pronounced in markets with low liquidity, as there may be fewer participants in the market, and the counterparty may not have the resources to fulfill their obligations.
Finally, traders must consider the potential for market manipulation when adding liquidity to a market. Market manipulation artificially inflates or deflates prices to benefit from the resulting price movements.
This practice is illegal in most markets, but it can still occur in markets with low liquidity, as there may be fewer participants, and it may be easier for a single trader to manipulate the market.
Why is liquidity so important anyway?
Liquidity is crucial to any trading market for three primary reasons: ensuring smooth market functionality, mitigating risks, and stabilizing the market.

1. Ensuring Smooth Market Functionality.
Consider a highly liquid stock like Apple (AAPL). Because it’s heavily traded on major stock exchanges like the NASDAQ, investors can swiftly buy or sell shares without causing large price swings.
This liquidity ensures that even large trades can be executed efficiently.
Buying or selling a large block of shares for a thinly traded penny stock with low liquidity could significantly increase the price. This would make it harder to determine accurate price / value.
And that is sort of what happened with the Gamestop stock a few years ago.
2. Mitigating Risks.
The bid-ask spread is typically narrow when trading a liquid stock like Microsoft (MSFT). This means lower transaction costs for traders than less liquid stocks, where spreads can be wider.
Liquid stocks like Alphabet (GOOGL) tend to experience less price volatility because buyers and sellers constantly flow. Even during turbulent market conditions, investors can easily enter or exit positions in these stocks, reducing the likelihood of extreme price swings.
3. Market Resilience and Stability.
During stressful situations like economic downturns or geopolitical events, liquid stocks like Facebook (FB) are less prone to abrupt price movements. This resilience keeps the market stable and participants willing to buy or sell shares.
Liquidity in widely traded stocks promotes market transparency and integrity. With ample liquidity, it’s harder for a single entity to manipulate prices or engage in fraudulent activities without being noticed.
Conclusion
In conclusion, adding liquidity and taking liquidity are both important aspects of trading. Adding liquidity helps ensure that the market is liquid and that there is enough supply and demand to stabilize prices.
On the other hand, liquidity allows traders to take advantage of price discrepancies and capitalize on short-term opportunities. Both strategies can generate profits, but it is important to understand the risks and rewards associated with each before making any decisions.